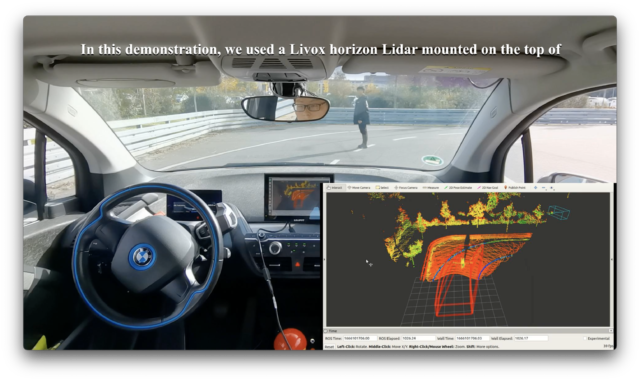
This video shows the autonomous driving and path tracking with pedestrian detection using Livox Lidar. In this demonstration, we used a Livox horizon Lidar mounted on the top of the BMW-i3 to detect pedestrians and vehicles based on a deep learning algorithm. In the right bottom corner of the video shows the point cloud and the detection result of the Lidar.
We virtualized a 3D space in the point cloud to represent the vehicle’s possible driving trajectory space in the next period of time. If there is no pedestrians or obstacles in this 3D space, it is green, but if a pedestrian breaks into this 3D space, then it will turn red and the vehicle will stop moving forward. If the pedestrian goes out, the vehicle will keep going. This 3D space is synchronized in real time with the current position of the vehicle, which is obtained from a Simulink program. In this demonstration, the vehicle is controlled by a Simulink program run on a laptop, and the pedestrian detection program is run on a Nvidia Jetson, which is written in Python and driven by ROS, these two computers communicate with each other using TCP/IP protocol.
本视频展示了无人驾驶和轨迹跟踪以及使用Livox激光雷达实现在驾驶过程中的行人检测。在该演示中,我们使用了一个安装在BMW-i3顶部的Livox horizon激光雷达,并通过基于深度学习的算法来实现行人和车辆的检测。在右下角的示图中,显示的是激光雷达的点云和检测结果。
我们在点云中虚拟了一个三维空间来表示车辆在接下来的一段时间内可能的行驶轨迹,如果在空间中没有行人或者障碍物,那么这个三维空间的外框是绿色的,如果有行人闯进该空间,则会变成红色,同时会控制车辆停止前进,当行人走出这个三维空间时,车辆会继续前进。这个三维空间是与在Simulink的程序中所计算得到的车辆位置实时同步的。在该演示中,车辆控制是通过一个在笔记本上运行的Simulink程序来实现的,而基于激光雷达点云的行人检测是由Nvidia Jetson上的一个基于ROS和Python的程序来实现的,这两个电脑之间通过TCP/IP来进行实时通讯。